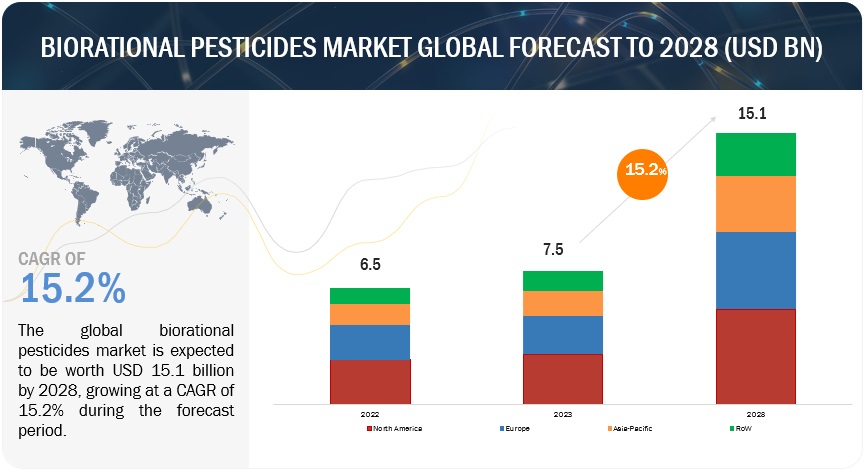
The biorational pesticides market size is anticipated to expand from USD 7.5 billion in 2023 to USD 15.1 billion by 2028, achieving a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.2% throughout the forecast period. This growth is driven by a growing awareness of the detrimental impacts that synthetic chemical pesticides have on ecosystems, biodiversity, and human health, prompting a shift towards more eco-friendly alternatives. Regulatory bodies are increasingly promoting biorational pesticides due to their lower toxicity and reduced environmental persistence compared to synthetic chemicals, which is fueling market growth.
Biorational Pesticides Market Trends
Here are some current trends in the Biorational Pesticides Market:
- Increased Demand for Sustainable Agriculture: As sustainability becomes a priority, there is a growing demand for biorational pesticides due to their eco-friendly and non-toxic characteristics. They offer a safer alternative to synthetic chemicals in pest management, aligning with organic and sustainable farming practices.
- Technological Advancements: Innovation in biotechnologies, such as microbial pest control agents and botanicals, has expanded the effectiveness of biorational pesticides. These advances are making them more competitive with conventional pesticides.
- Rising Organic Farming Practices: The global shift towards organic farming is boosting the biorational pesticides market. Farmers are looking for pest control methods that comply with organic certification standards, leading to a higher adoption of biorational products.
- Supportive Regulatory Environment: Regulatory bodies in various countries are promoting the use of environmentally safe pesticides, driving the demand for biorational alternatives. Governments are also providing incentives for research and development in this area.
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Adoption: Biorational pesticides are gaining popularity within integrated pest management systems because they are less likely to harm beneficial insects and help maintain ecological balance.
- Growing Awareness About Health and Safety: With rising concerns over the harmful effects of chemical pesticides on human health and the environment, there is increasing consumer and farmer awareness about the benefits of using biorational pesticides.
- Market Penetration in Developing Regions: The adoption of biorational pesticides is increasing in emerging markets, especially in regions like Asia-Pacific and Latin America, driven by expanding agricultural activities and increased awareness of sustainable practices.
Biorational Pesticides Market Drivers: Chemical pesticide ban and awareness programs by government
The negative effects of chemical pesticides on soil, the environment, and water bodies worldwide have prompted a shift toward biopesticides in agriculture. This shift is supported by awareness campaigns and policies aimed at creating a conducive environment for private sector participation. In regions such as South America, Asia Pacific, and Europe, rapid market growth is being observed, driven by initiatives that encourage both farmers and producers to adopt and produce biorational pesticides.
In North America, the markets for bioinsecticides, biofungicides, and bionematicides—specific categories of biopesticides—are regulated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). The EPA is responsible for overseeing their registration and monitoring their impact on human health and the environment. The sale and distribution of biopesticides are governed by the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA), which ensures compliance with the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FFDCA) to guarantee the safety of food and feed free from harmful residues.
Biorational Pesticides Market Growth Driven by Botanical Sources: Enhanced Storage and Broad-Spectrum Effectiveness Against Pests
Botanical-based pesticides, which are derived from plant sources or their extracts, often demonstrate enhanced stability during storage. These plant-derived compounds typically exhibit inherent stability, reducing the likelihood of rapid degradation or breakdown under standard storage conditions. As a result, they generally have a longer shelf life compared to some microbial-based pesticides.
When it comes to storage requirements, botanical-based pesticides usually necessitate simpler conditions than their microbial counterparts. While they do require standard storage practices—such as avoiding extreme temperatures and excessive moisture—they typically do not need specialized storage facilities or strict environmental controls.
Additionally, many botanical-based pesticides possess a broad-spectrum effect, allowing them to target and control a wide variety of pests. These pesticides may contain compounds that affect numerous types of insects, fungi, and other pests. For example, plant-derived compounds like pyrethrins and neem oil can influence a wide range of insects and diseases, providing a comprehensive strategy for effective pest control.
What factors are contributing to the growth of the biorational pesticides market in North America?
The agricultural landscape in North America features a mix of farming systems, ranging from large-scale commercial enterprises to smaller organic and specialty crop operations. This diversity creates optimal conditions for the adoption of biorational pesticides across various crops.
Regulatory agencies in North America have established strong frameworks to closely monitor the use of conventional pesticides, driven by concerns about safety and environmental impact. As a result, there has been a notable increase in the demand for biorational pesticides, which are valued for their safety and environmentally friendly qualities. A significant development occurred when the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) took steps to protect children and agricultural workers from the dangers of a harmful pesticide linked to long-lasting cognitive impairments.
Top Biorational Pesticides Companies:
The key players in the biorational pesticides market include BASF SE (Germany), Bayer AG (Germany), UPL (India), FMC Corporation (US), Syngenta AG (Switzerland), Novozymes A/S (Denmark), Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd (Japan), Pro Farm Group Inc (US), Koppert (Netherlands), Valent BioSciences LLC (US), Gowan Company (US), Certis Biologicals (US), Biobest Group (Belgium), BIONEMA (UK), and Vestaron Corporation (US).