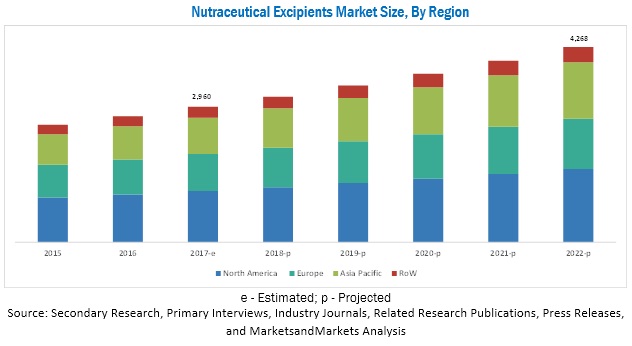
The nutraceutical excipients market is estimated at USD 2.96 Billion in 2017 and is projected to reach a value of USD 4.27 Billion by 2022, at a CAGR of 7.6%. The market is driven by factors such as the growing demand for nutraceuticals and advances in nanotechnology used in imparting new functions to excipients. The major players in the food industry are investing in research & development activities to expand their excipient product portfolios and attract more consumers by providing innovative products at lower prices.
Advances in nanotechnology imparting new functions to excipients
Nanotechnology-enabled drug delivery systems (NDDS) are used to tackle the issue of drug toxicity. There are two major approaches in using nanotechnology as a drug delivery system (DDS). The first is to reduce the size of nutraceutical drug crystals to ensure greater solubility and bioavailability, while the second approach is using some form of nano-carrier for the more effective delivery of the active ingredient.
Poor drug physiochemical properties can be improved by associating the drug with a pharmaceutical carrier. A drug delivery system (DDS) can enhance a drug’s pharmacokinetics and cellular penetration. Moreover, drug delivery system (DDS) may also address obstacles arising from low drug solubility, degradation, fast clearance rates, nonspecific toxicity, and inability to cross biological barriers. Hence, the use of nanotechnology in improving the functionality of excipients is also expected to drive growth of the nutraceutical excipients market.
Download PDF Brochure: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=247060367
Difficulties in product formulation
Nutraceutical formulations, unlike pharmaceutical formulations, have presence of more active ingredients in higher weights, thereby resulting in limited room for excipients. Generally, nutraceutical formulations have 70–90% active ingredients with the remaining being excipients, whereas traditional pharmaceutical formulations have 70–90% excipients with the remaining 10–30% being active ingredients. For nutraceutical formulations, this low percentage of excipients and a high percentage of actives make it difficult to achieve certain desired results in the final product, such as disintegration time, hardness, and friability. In addition, consumers are increasingly demanding a smaller dosage size of nutraceutical products and the use of clean ingredients including excipients in the product, which further restrict the options for formulators, thereby making it more difficult to formulate and attain the desired product outcomes.
The proteins & amino acids segment accounted for the largest share of the nutraceutical excipients market, by functionality, in 2016.
On the basis of functionality, proteins & amino acids accounted for the largest share of the nutraceutical excipients market in 2016, followed by the omega-3 fatty acids. Excipients are necessary during the manufacturing of protein-based nutraceutical products to avoid protein aggregation. Excipients are also used in the manufacture of amino acid-based nutraceutical products; for instance, in the powder form of the amino acid supplement, they are used for the powder to dissolve easily and give it an acceptable taste.
Speak to Analyst: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/speaktoanalystNew.asp?id=247060367
North America dominated the nutraceutical excipients market in 2016.
North America accounted for the largest market share in 2016. The nutraceutical excipients market is consolidated in North America and dominated by a few companies such as DuPont, Kerry, Cargill, and Ingredion. The market for nutraceutical excipients here is mature, and hence, the growth is moderate compared to other regions.
This report includes a study of marketing and development strategies, along with the product portfolios of the leading companies. It includes profiles of leading companies such as Kerry (Ireland), ABF (UK), DuPont (US), Ingredion (US), and Sensient (US), Roquette Frères (France), Meggle (Germany), Hilmar Ingredients (US), JRS Pharma (Germany), Innophos (US), Cargill (US), and IMCD (Netherlands).
