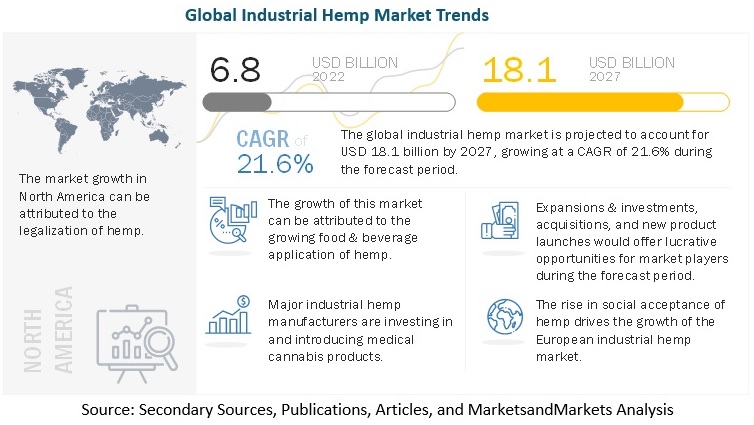
The global industrial hemp market size is estimated to be valued at USD 6.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach USD 18.1 billion by 2027, recording a CAGR of 21.6% in terms of value. Industrial hemp is defined as the plant Cannabis sativa L. and any part of such plant, whether growing or not, with a delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) concentration of not more than 0.3% on a dry weight basis. As industrial hemp contains less than 0.3% tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), it has a wide range of applications in the textile, food, and beverage, construction, animal care, personal care, pharmaceutical, paint, lubricant, bioplastic, and biofuel industries. One of the major drivers of the global industrial hemp market is the legalization of hemp cultivation in various countries.
Download PDF brochure: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=84188417
Leading players profiled in this report:
• Marijuana Company of America Inc. (US)
• Cronos Group Inc. (Canada)
• Ecofibre Limited (Australia)
• Green Thumb Industries (US)
• Curaleaf Holdings Inc. (US)
• GenCanna (US)
The European region is projected to grow at the highest CAGR during the forecast period
In the forecasted period, the European region will be the fastest growing. The area dedicated to hemp cultivation in the EU has increased significantly in recent years, rising 75% from 19.970 ha in 2015 to 34,960 ha in 2019. France has the largest agricultural area dedicated to hemp cultivation in the EU, with nearly 18,000 hectares, followed by Italy, the Netherlands, and Estonia. Simultaneously, hen production increased by 62.4%, from 103,750 tons to 168,455 tons. France produces the most, accounting for more than 70% of EU output, followed by the Netherlands (10%) and Austria (4%). In Europe, hemp fibers are primarily used for specialty pulp and paper, with applications ranging from cigarette paper to Bible paper, bank notes, and technical filters.
By type, increase in the popularity of hemp bast drives the growth of industrial hemp market
Hemp bast fibers are cellulosic fibers found in the phloem of bast fiber crops such as industrial hemp which are natural fibers derived from plants. The main components of hemp bast fibers are cellulose (53-91%), hemicellulose (4-18%), lignin (1-21%), and pectin (1-17%). The benefits of bast fibers include lighter product weight, lower energy consumption, and a smaller environmental footprint. Bast fibers can be spun and woven and are thus widely used in the textile industry.
Request Sample Pages: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/requestsampleNew.asp?id=84188417
By application, there is an increased use of industrial hemp in animal nutrition, driving the growth of the industrial hemp market
Hemp production produces byproducts, one of which is hemp meal. Because of its high fiber, fat, and protein content, hemp meal is a potential feedstuff for animal agriculture and a possible substitute for soybean meal in many livestock diets. Furthermore, hemp products face regulatory hurdles before they can be legally incorporated into livestock feedstuffs, due to concerns that tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), found in hemp biomass, could be transferred to animal products intended for human consumption.

