The smart irrigation industry has emerged as a vital component of modern agricultural and water management practices. It combines cutting-edge technology, such as sensors, controllers, and Internet of Things (IoT) platforms, to optimize water usage efficiently. Unlike traditional irrigation methods, smart irrigation systems deliver water precisely where and when it is needed, reducing wastage and ensuring that crops receive optimal hydration. As global water scarcity becomes a pressing issue, the adoption of smart irrigation systems is gaining momentum across agriculture, landscaping, and urban green spaces.
Download PDF Brochure @ https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=199758913
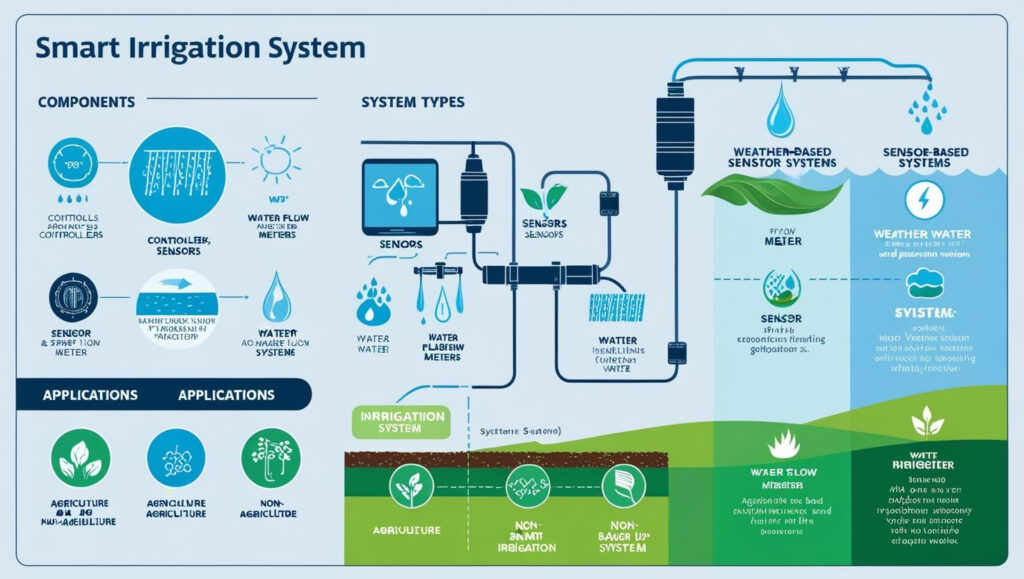
Key Components of Smart Irrigation Systems
Smart irrigation systems consist of several key components that work together to enhance water management:
- Sensors:
Sensors are the eyes and ears of smart irrigation systems, collecting real-time data on soil moisture levels, temperature, humidity, and other environmental factors. These sensors provide critical insights that help determine the exact amount of water required by plants. - Controllers:
Controllers act as the brain of the irrigation system. They process data from sensors and external sources, such as weather forecasts, to create precise irrigation schedules. Modern controllers often feature advanced algorithms and wireless connectivity, allowing users to manage irrigation remotely via mobile apps or cloud-based platforms. - Valves and Actuators:
Valves and actuators control the flow of water from irrigation systems. These components ensure that water is distributed efficiently and accurately based on data from sensors and controllers. - Water Management Platforms:
Cloud-based and IoT platforms collect and analyze data from sensors to provide actionable insights. These platforms enable users to monitor irrigation systems in real-time, make adjustments remotely, and track water usage.
Sensors and Controllers for Smart Irrigation
The role of sensors and controllers is central to the functionality of smart irrigation systems. Sensors measure critical parameters like soil moisture, temperature, and light, while controllers use this data to automate water delivery. Advances in sensor technology, such as soil moisture sensors, weather sensors, and evapotranspiration (ET) sensors, have made irrigation systems more accurate and responsive.
Similarly, controllers have evolved from simple timers to sophisticated devices equipped with AI and IoT capabilities. These smart controllers can now analyze large datasets, predict future water needs, and adjust irrigation schedules accordingly. By integrating real-time data from sensors, controllers help optimize water usage, reduce wastage, and improve crop health.
The Impact of Big Data on Irrigation Practices
Big data has revolutionized irrigation practices by enabling more informed and data-driven decision-making. Smart irrigation systems generate massive amounts of data from sensors, weather forecasts, and soil analytics, which, when processed, provide valuable insights into water management. This wealth of information allows farmers and land managers to:
- Predict Water Needs: Big data analytics can forecast water requirements based on weather patterns, soil type, and crop growth stages, ensuring water is applied only when necessary.
- Optimize Resource Allocation: With data-driven insights, farmers can optimize water allocation across different fields, reducing wastage and maximizing productivity.
- Monitor Water Usage: Continuous data collection and analysis allow for real-time tracking of water usage, helping stakeholders detect inefficiencies and make timely adjustments.
As big data continues to shape the future of agriculture, smart irrigation systems will increasingly rely on predictive analytics to enhance efficiency, sustainability, and yield.
Future Trends and Growth Opportunities
The future of the smart irrigation industry looks promising, with several emerging trends and growth opportunities shaping its evolution:
- Integration of AI and Machine Learning:
Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms are enabling smarter irrigation systems that can analyze vast datasets, predict water needs, and make real-time adjustments autonomously. - Rise of IoT-Enabled Smart Cities:
As urban areas expand, the integration of smart irrigation systems in cities is growing, with municipalities using these technologies to maintain green spaces and public gardens efficiently. - Focus on Renewable Energy:
The use of solar-powered irrigation systems is on the rise, driven by the need for sustainable and eco-friendly water management solutions. Renewable energy-powered irrigation systems will expand access to irrigation in remote and off-grid areas. - Adoption in Emerging Markets:
In regions facing water scarcity, such as Africa, Asia, and the Middle East, smart irrigation systems offer an opportunity to enhance water use efficiency, food security, and sustainable agriculture practices.
Maintenance and Management of Smart Irrigation Systems
Proper maintenance and management are crucial to ensuring the longevity and efficiency of smart irrigation systems:
- Regular Calibration of Sensors: Sensors need to be calibrated periodically to ensure accuracy in measuring soil moisture and other environmental conditions.
- Periodic System Audits: Conducting regular system audits helps identify any malfunctions or inefficiencies in the irrigation process, such as broken pipes or blocked valves.
- Software Updates: Keeping controllers and software platforms updated ensures they operate at peak performance and benefit from the latest technological advancements.
- Cleaning and Inspection: Regular cleaning of irrigation components, including filters and nozzles, is essential to prevent clogging and ensure optimal water distribution.
Challenges and Opportunities in the Smart Irrigation Industry
The smart irrigation market faces several challenges, which can also present unique opportunities for growth:
- High Initial Costs:
The upfront investment required for smart irrigation systems can be a deterrent, especially for small-scale farmers. However, as technology becomes more affordable, these systems are becoming accessible to a wider audience. - Lack of Awareness:
Many potential users remain unaware of the benefits of smart irrigation systems. Educating farmers and landowners about the long-term economic and environmental advantages can drive adoption. - Connectivity Issues:
In remote or rural areas, limited internet access and unreliable cellular networks can hinder the functionality of IoT-enabled irrigation systems. Developing solutions that work offline or leverage alternative connectivity methods could address this challenge. - Regulatory Support:
Government initiatives promoting water conservation and sustainability provide opportunities for smart irrigation adoption. Policies and subsidies can play a pivotal role in encouraging wider use of these systems.
The smart irrigation industry is poised for significant growth as it addresses global challenges such as water scarcity, agricultural productivity, and sustainability. By leveraging technologies like IoT, AI, and big data, smart irrigation systems are becoming increasingly sophisticated, efficient, and accessible. Despite challenges such as high costs and connectivity limitations, the opportunities for innovation, expansion into emerging markets, and sustainable water management are driving the industry toward a more sustainable future. As stakeholders continue to invest in these technologies, smart irrigation will play a key role in enhancing water use efficiency and food security worldwide.