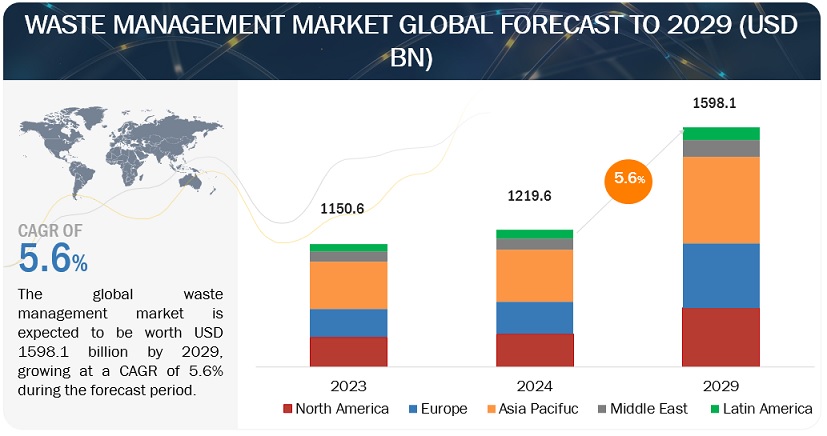
The report “Waste Management Market by Waste (Hazardous, E-waste, Plastic, Bio-medical), Service (Open dumping, Incineration, Landfill, Recycling), End User (Residential, Commercial, Industrial) and Region – Global Forecast to 2026″, size is expected to grow from an estimated USD 423.4 billion in 2021 to USD 542.7 billion by 2026, at a CAGR of 5.1%, during the forecast period. The key drivers for the waste management market include stringent regulations of governments worldwide for better management of waste and initiate environmental protection; strong focus of several governments to conduct awareness programs showcasing importance of waste segregation and waste management; technological advances and shortened life cycle of electronic products help in increasing e-waste.
By end user, the residential segment is the largest contributor in the waste management market during the forecast period.
The residential segment is estimated to lead the waste management market. Asia Pacific was the largest market for residential end user segment in 2020 Ever-increasing population and significant solid waste generation to drive demand for waste management services from residential segment. The other key drivers for the growth of the waste management market for the residential sector are that the waste generated from residential end users can be used for generating energy through waste-to-energy plants by burning solid waste to produce steam in a boiler and can also be is used to generate electricity. There are different types of waste-to-energy systems or technologies. The most common type used in the US is the mass-burn system, where unprocessed solid waste is burned in a large incinerator with a boiler and a generator for producing electricity.
Download PDF Brochure @ https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=72285482
By waste type, the e-waste segment is expected to be the largest contributor during the forecast period.
The e-waste segment is estimated to lead the waste management market during the forecast period. E-waste includes electrically powered component waste. They include appliances such as computers, consumer electronics, and refrigerators. E-waste is a mixture of useful and hazardous materials that demand careful handling and recycling of materials. Thus, e-waste management has gained importance globally to secure the environment from the adverse effects of the materials such as lead and plastics. The recycled material is used to make next-generation goods. The market for waste segment is driven by the rapid urbanization, transforming urban mobility, and increased need to reduce carbon emissions offered by the segment. Asia Pacific is estimated to hold the largest share of the waste management market, followed by North America because of the growing usage of appliances that use electricity are expected to drive the market for waste management market.
By service type, the landfill segment is expected to be the largest contributor during the forecast period.
The landfill held the largest share of the waste management market, by waste type in 2020. The growth of the landfill segment is driven by the Increased Need to dispose of waste that cannot be recycled. Landfills offer various advantages, such as it offers good energy sources; it is an eco-friendly option; it keeps cities, towns, and districts clean, and helps keep hazardous waste segregated; it is a relatively cheaper option for waste management. The market for the landfill segment in Asia Pacific is expected to grow at the 7.2% CAGR during the forecast period.
Request Sample Pages @ https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/requestsampleNew.asp?id=72285482
Asia Pacific is expected to be the largest and fastest-growing market during the forecast period.
Asia Pacific accounted for the largest share of the global waste management market in 2020. The region has been segmented, by country, into China, Japan, India, Australia, South Korea, and Rest of Asia Pacific. Rest of Asia Pacific mainly includes Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand, and Indonesia. The population growth in the region, the high disposable income of the people, and the increased demand for packaged food products are among a few major factors that drive the growth of waste management in the region. Asia Pacific is also a key contributor to marine plastic pollution. The materials involved include plastic bottles, plastic bags, single-use plastic items, and plastic packaging, among others. Key countries responsible for this kind of pollution include China, Indonesia, and Thailand.
In addition, the rise in well-being and prosperity of urban residents is linked closely to increased consumption and production patterns with consequences for waste streams. Increased municipal solid waste is particularly noticeable in low- and middle-income countries. In these countries, the rate of waste generation has risen quickly and is expected to accelerate over the next decade and beyond. According to the United Nations’ Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UNESCAP), between 50% and 65% of municipal solid waste in low- and middle-income countries is organic and can be turned into high-quality compost for use in agriculture, gardening, or landscaping or converted to biogas to produce heat and electricity. There are also significant opportunities for recycling inorganic materials, such as glass, plastic, and metal. Moreover, the manufacturing of new glass‐based materials also has an ultimate opportunity for open‐loop recycling and has more environmental benefits than that of landfilling. Between 25 and 35% of municipal solid waste is recyclable inorganic waste; this proportion will increase over the coming decades with further development of countries, leading to rising demand for waste management.
The key players in the waste management market include companies such as Waste Management (US), Veolia (France), Republic Services (US), SUEZ (France), and Waste Connections (US).

